What is Docker?
Docker is a platform for developing, building and shipping the application using Container Virtualization Technology.
What Docker Consists of?
Docker Platform itself composed of many tools:
>>Docker Engine
>>Docker Machine
>>Docker Hub
>>Docker Swarm
>>Docker Compose
>>Kitematic
[Note: Container Virtualization uses kernel on host to create multiple containers. From outside it looks like we are dealing with VMs and not containers. But it is not.
We may be using the term hypervisor at many places below and a short note on what hypervisor is. A hypervisor or virtual machine monitor (VMM) is a piece of computer software [Ex. VMware VSphere], firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines.
A computer on which a hypervisor is running one or more virtual machines is defined as a host machine. Each virtual machine is called a guest machine. ]
Why Docker?
>>Docker interacts directy with the Kernel of Host OS whereas the hypervisor are something installed on the Host and operates based on the Guest Instances sharing the Hardware Resources.
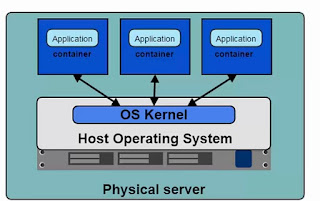 |
| Docker Architechture |
 |
| Hypervisor Architechture |
- Containers interact directly with Host Kernel.
- Containers are lightweight and can be started quick.
- Containers requires less CPU and RAM to Start up. Thus we can have more Containers.
- It's nothing but the boot2Docker that helps us setup the Virtual Linux Box, place Docker Engine within and Configure Container to talk to this Engine.
- Docker Machine act the Docker Host.
Docker Engine:
Also referred as Docker Daemon.
- It's a program that enables the Containers to be built, shipped and run.
- The Docker Engine uses Linux-specific kernel features. We can relate just like the one below if our OS is Windows / Mac.
 |
| Docker Engine |
- Thus we install boot2Docker that sets up the Virtual Linux Box and have the Docker Engine placed with in.
Docker Client
- Docker clients helps in interacting with the Docker Server/ Docker Engine/
- Docker Client fetch the Input from User and pass the details back to Docker Daemon for processing.
- Docker Client and the Docker Machine(boot2Docker) in most of the cases are installed in the same host. Here it is the OS Platform that we use.
- If not happy with Command line docker, we also opt for Kitematic that GUI Tool for interacting with Docker daemon.
[Note: command docker version on container returns the Daemon Version and the Docker Version]
Containers Vs Images:
Images are read only Templates used to create the Containers. Stored in Local or the Docker Hub. While Containers are the Application Platform made up of multiple images.
Docker Registry/Hub Vs Repository:
Images can be stored in the registry/ Docker Hub. The registry holds multiple repositories and repository holds multiple images.
Example: Docker Hub Public Registry - https://registry.hub.docker.com
Image fetched from repository is run using docker run [repo_name: tag_name] command
How to create the Docker Engine?
Gets Automatically created if not created at the start of the boot2Docker terminal. This is just a general info.
Step 1: Run the common in terminal boot2Docker delete
Step 2: boot2Docker init - brings up the Docker Engine.
Step 3: boot2Docker up - starts the Docker Engine and would make it run.
Step 4: boot2Docker ip - brings the IP Address
Common Docker Commands:
docker run [repo_name: tag_name of image] -> Fetch the Image and installs in the Container.
docker start name_of_container -> Starts the Container.
docker stop name_of_container -> Stops the Container.
docker ps [-a include stopped containers] -> Lists all the Containers.
docker rm <image | id> -> Remove a Container.
docker login Login the Containers with Docker Hub Credentials.